Without more data, a black hole’s origins can be spun in any direction
Researchers say that current results depend on models rather than data.
Clues to a black hole's origins can be found in the way it spins,...
It’s time for mysterious spokes to appear in Saturn’s rings
The Hubble Space Telescope recently captured the appearance of several asymmetrical ‘spokes’ rising above the rings of Saturn, marking a coming change in season...
Scientists detect a new ring system in our Solar System
Scientists have discovered a new ring system around a dwarf planet on the edge of the Solar System.
NASA’s Curiosity finds surprise clues to Mars’ watery past
Among other discoveries made by the rover, rippled rock textures suggest lakes existed in a region of ancient Mars that scientists expected to be...
Astronomers still scratching their heads over population of ocean-world exoplanets
So, what were the most significant results pertaining to water worlds around M-dwarf stars?
Space dust could help protect the earth from climate change
A new study led by scientists at the Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian and the University of Utah explores the potential of using space dust to shield sunlight.
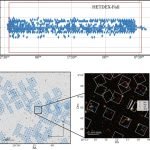
Astronomers reveals galaxy gold mine in first large survey
Over 200,000 astronomical objects including distant stars and galaxies have been mapped in 3D for the first time.
Astronomers have barely scratched the surface of...
Scientists detect a black hole table for two
Astronomers have discovered a galactic table for two—a pair of unusually close black holes that are feeding together after their respective galaxies collided.
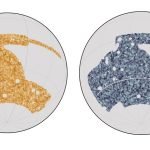
Astronomers make a new map of all the matter (and dark matter) in the...
There’s a lot of matter in the Universe, but not all of it is visible to us.
Matter is, essentially, anything that has mass and...
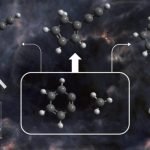
Scientists reveal the chemical secret of star birth
Scientists have uncovered what might be a critical step in the chemical evolution of molecules in cosmic “stellar nurseries.”