Earth & Environment
Why dance tracks dominate TikTok while love songs rule Spotify
What makes a song become a hit today?
While listeners certainly play a role, new research suggests that streaming platforms and their algorithms also have...
US is less prone to oil price shocks than in past decades
Oil is a global market, so when prices rise in one place, they rise everywhere. The current war against Iran has already raised oil...
Scientists grow chickpeas in “moon dirt,” opening the door to farming on the Moon
As NASA prepares for future missions that could send astronauts back to the Moon, scientists are trying to answer an important question: what will...
Elephants steer clear of humans much more than other wildlife, study finds
Wild animals do not all react to human activity in the same way.
A new study from Botswana shows that some species are much more...
Antarctica has lost ice the size of 10 Los Angeles cities in 30 years
A new 30-year study has revealed how Antarctica’s ice is slowly retreating along parts of its vast coastline.
Scientists led by researchers at the University...
Did the first land plants accidentally trigger two ancient ocean extinctions?
Hundreds of millions of years ago, the first plants began spreading across Earth’s land. This major turning point helped transform the planet into the...
Fossil bite marks reveal ancient predator hunts 280 million years ago
New research suggests that large land predators were already hunting big plant-eating animals more than 280 million years ago, much earlier than scientists once...
Mars Express reveals a landscape filled with ancient craters on the red planet
A new image captured by the Mars Express orbiter offers a striking view of one of the most heavily cratered regions on Mars.
The image...
Wildfire smoke may trigger more severe strokes
Air pollution is often thought of as a long‑term environmental problem, but new research suggests that even short bursts of polluted air may have...
Study finds doctors more likely to die at home
Many people wonder whether doctors make different choices about medical care at the end of life.
Because physicians understand diseases, treatments, and hospital systems better...
‘Forever chemicals’ may speed up aging in middle-aged men
Chemicals known as PFAS, often called “forever chemicals,” are found in many everyday products, from non-stick cookware and waterproof clothing to food packaging and...
How long do civilizations last
It is one of the most famous questions in science, and it was asked, as legend has it, over lunch.
Enrico Fermi, the physicist who...
FEATURED
A 40-million-year-old ant hidden in Goethe’s amber still has stories to tell
More than 200 years after Johann Wolfgang von Goethe’s death, his curiosity about nature is still leading to new discoveries.
Scientists in Germany have now...
Ants in your house? Here’s how they get everywhere—even high up in tall buildings
Ants are among nature's greatest success stories, with an estimated 22,000 species worldwide.
Tropical Australia in particular is a global hotspot for ant diversity. Some...
The Southern Ocean has the cleanest air on Earth. We have just discovered why
The Southern Ocean is renowned for having the cleanest air on Earth. But the precise reasons why have remained a mystery, until now.
There’s more to...
Air pollution linked to increased dementia risk
A major new study has found that long-term exposure to air pollution—such as emissions from cars and industry—can significantly increase the risk of developing...
Americans’ IQ scores are lower in some areas, higher in one
IQ scores have substantially increased from 1932 through the 20th century, with differences ranging from three to five IQ points per decade, according to...
Tiny parasitic worm could help save Chesapeake bay’s blue crabs
A parasitic worm that lives on the eggs of female blue crabs might actually help scientists and fishery managers protect this iconic species in...
Scientists discover cats and dogs have evolved baby faces in surprising similar ways
In a surprising new study, scientists have found that some cats and dogs have evolved to look unusually alike—despite being very different animals.
These similarities...
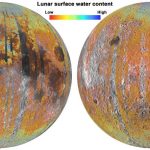
Did the Moon’s water come from Earth?
A recent study published in Nature Astronomy examines how processes within the Earth’s magnetic field could be contributing to the formation of water on...