Arthritis is a condition that causes pain, swelling, and stiffness in the joints. It can make everyday activities challenging and affect the quality of life.
There are many types of arthritis, but the most common ones are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Understanding the various treatments available can help manage the symptoms and improve life for those affected.
One of the primary ways to treat arthritis is through medications. Pain relievers like acetaminophen (Tylenol) and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen (Advil) or naproxen (Aleve) are commonly used to reduce pain and inflammation.
Research has shown that these medications can be effective in relieving arthritis symptoms, but they should be used as directed by a healthcare provider to avoid potential side effects.
For more severe pain, doctors may prescribe stronger medications like opioids. However, due to the risk of addiction and other side effects, these are usually used only when other treatments haven’t worked.
Another type of medication, corticosteroids, can also help reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system. Corticosteroids can be taken orally or injected directly into the affected joint, and studies have found them to be effective in managing severe arthritis symptoms.
Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) are commonly used for rheumatoid arthritis. These medications slow down the disease’s progression and help prevent joint damage.
Methotrexate is one of the most commonly prescribed DMARDs, and research has shown it to be effective in controlling rheumatoid arthritis symptoms. Biologic response modifiers, a newer class of DMARDs, target specific parts of the immune system to reduce inflammation.
These medications, such as adalimumab (Humira) and etanercept (Enbrel), have been shown to be effective in managing rheumatoid arthritis and improving quality of life.
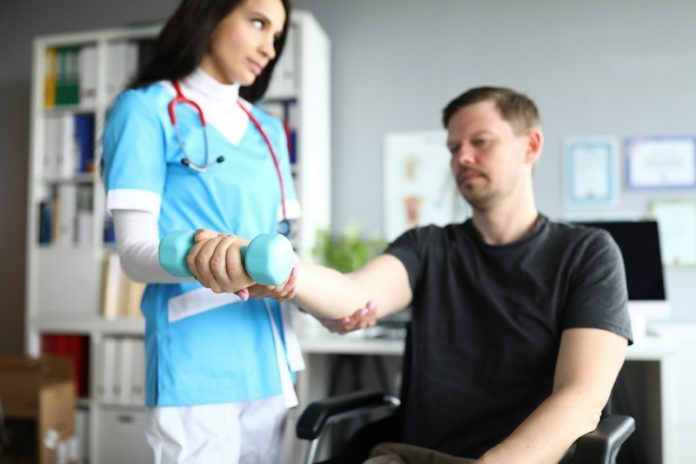
Physical therapy is another important part of arthritis treatment. A physical therapist can design a personalized exercise program to help strengthen the muscles around the joints, improve flexibility, and reduce pain.
Studies have shown that regular physical activity can help reduce arthritis symptoms and improve overall joint function. Low-impact exercises like swimming, walking, and cycling are particularly beneficial for people with arthritis because they are easier on the joints.
In addition to physical therapy, occupational therapy can help people with arthritis manage their daily activities. An occupational therapist can teach techniques to reduce strain on the joints, such as using assistive devices and making modifications to the home or workplace.
Research has found that occupational therapy can improve the ability to perform daily tasks and enhance the quality of life for people with arthritis.
Lifestyle changes can also play a significant role in managing arthritis. Maintaining a healthy weight is important because excess weight puts additional stress on the joints, particularly the knees, hips, and spine.
Studies have shown that weight loss can significantly reduce pain and improve joint function in people with arthritis. Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can also help reduce inflammation and support overall health.
Some people find relief from arthritis symptoms through complementary therapies like acupuncture, massage, and chiropractic care. Research on these therapies is mixed, but many individuals report improved pain and mobility.
Acupuncture, in particular, has been found in some studies to reduce pain and improve function in people with osteoarthritis. It involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to stimulate natural pain-relieving mechanisms.
Surgery is considered a last resort when other treatments have not been effective. Joint replacement surgery, such as hip or knee replacement, can significantly reduce pain and improve function for people with severe arthritis.
Research has shown that joint replacement surgery can lead to substantial improvements in quality of life and mobility. However, it is a major procedure with risks, and recovery can take several months.
In summary, treating arthritis involves a combination of medications, physical and occupational therapy, lifestyle changes, and, in some cases, surgery. Pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs, and DMARDs can help manage symptoms and slow disease progression.
Physical and occupational therapy can improve joint function and make daily activities easier. Maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, and considering complementary therapies can also provide relief.
For those with severe arthritis, joint replacement surgery may be an option. Understanding these treatments and working with healthcare providers to create a personalized plan can help people with arthritis lead more comfortable and active lives.
If you care about arthritis, please read studies about extra virgin olive oil for arthritis, and pomegranate: A natural treatment for rheumatoid arthritis.
For more information about arthritis, please see recent studies about how to live pain-free with arthritis, and results showing medical cannabis may help reduce arthritis pain, back pain.
Copyright © 2024 Knowridge Science Report. All rights reserved.



