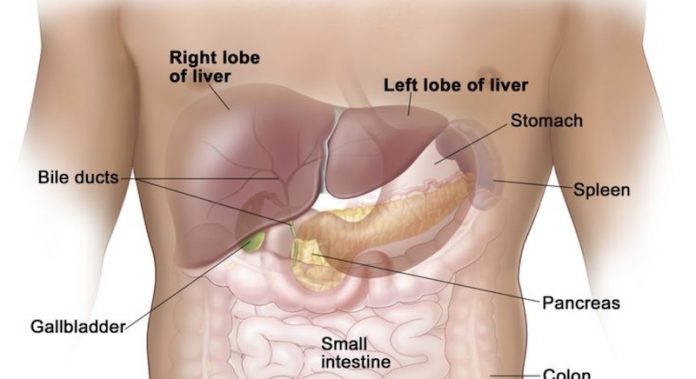
Liver cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the liver.
The liver is one of the largest organs in the body. It has two lobes and fills the upper right side of the abdomen inside the rib cage. Three of the many important functions of the liver are:
To filter harmful substances from the blood so they can be passed from the body in stools and urine.
To make bile to help digest fats from food.
To store glycogen (sugar), which the body uses for energy.
Liver cancer is not common in the United States, but it is common in other parts of the world.
Worldwide, liver cancer is the sixth most common cancer and the third leading cause of cancer death. It is most common in sub-Saharan Africa and parts of eastern Asia, including China, Hong Kong, and Taiwan.
In the United States, rates of liver cancer are lowest in White individuals and highest in American Indian/Alaska Native individuals.
The number of new cases of liver cancer continues to increase, making it the sixth leading cause of cancer deaths in the United States.
Finding and treating liver cancer early may prevent death from liver cancer.
Being infected with certain types of the hepatitis virus can cause hepatitis and may lead to liver cancer.
Hepatitis is most commonly caused by the hepatitis virus. Hepatitis is a disease that causes inflammation (swelling) of the liver. Damage to the liver from hepatitis that lasts a long time can increase the risk of liver cancer.
Hepatitis B (HBV) and hepatitis C (HCV) are two types of the hepatitis virus. Chronic infection with HBV or HCV can increase the risk of liver cancer.
Hepatitis B
HBV is caused by contact with the blood, semen, or other body fluid of a person infected with HBV virus.
The infection can be passed from mother to child during childbirth, through sexual contact, or by sharing needles that are used to inject drugs.
It can cause scarring of the liver (cirrhosis) that may lead to liver cancer.
Hepatitis C
HCV is caused by contact with the blood of a person infected with HCV virus. The infection can be spread by sharing needles that are used to inject drugs or, less often, through sexual contact.
In the past, it was also spread during blood transfusions or organ transplants. Today, blood banks test all donated blood for HCV, which greatly lowers the risk of getting the virus from blood transfusions.
It can cause scarring of the liver (cirrhosis) that may lead to liver cancer.
Sign up for our newsletter for more information about this topic.
If you care about liver health, please read studies about simple habit that can give you a healthy liver, and drug that may help protect against liver damage, obesity.
For more information about liver health, please see recent studies about how do sugary beverages affect the liver, and results showing that time-restricted eating may protect your liver health, blood sugar.
Source: National Cancer Institute