New COVID-19 vaccine shows strong promise in preventing COVID-19
In a new study, researchers found positive results that distinguish a new COVID-19 vaccine candidate from other vaccine candidates that are currently in advanced...
New study confirms link between flu and heart problems
The link between influenza and serious heart conditions just grew stronger.
In a new study, researchers examined more than 80,000 adult patients hospitalized with flu...
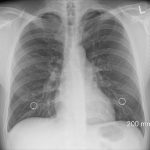
Many COVID-19 survivors may need a lung transplant in the future
Doctors are currently uncertain about the long-term effects of COVID-19 on the lungs of those who get the disease.
But they do know that patients...
COVID-19 vaccines are moving fast, but will Americans agree to get them?
Only one in three U.S. adults received the flu vaccine in 2018, a number that has critical implications for the impending flu season.
The flu...
Single-use N95 respirators can be decontaminated and used up to three times
N95 respirators, which are widely worn by health care workers treating patients with COVID-19 and are designed to be used only once, can be...
Scientists develop a fast, accurate, low-cost COVID-19 test
In a new study, researchers develop a new low-cost diagnostic test for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) that quickly delivers accurate results without the need...
Nurses over drivers? Elderly over youth?… Who gets COVID-19 vaccine first?
In a new study, researchers suggest in this age of coronavirus, with vaccine experimentation moving at a historic pace to the clinical trials phase,...
Drug hydroxychloroquine does not inhibit COVID-19 infection, scientists claim
In a new paper, researchers have come to the conclusion that chloroquine (CQ) and hydroxchloroquine (HCQ) are unlikely to provide clinical benefit against COVID-19.
The...
This hormone may reduce COVID-19 severity in women
Why are men at greater risk than women for more severe symptoms and worse outcomes from COVID-19 regardless of age?
In a new review study,...
Antiviral drug used to treat cat coronavirus may also treat COVID-19, study finds
In a new study, researchers say that a drug used to cure a deadly disease caused by a coronavirus in cats may also be...