Trending News
Latest Reports
Should I take vitamin C to ward off colds, lower blood pressure or reduce...
Vitamin C is one of the most iconic nutrients in popular health culture, often credited with preventing colds, boosting immunity and even fighting serious...
Brain immune cells may create Alzheimer’s plaques
Alzheimer’s disease is one of the most common causes of dementia worldwide. It slowly damages memory, thinking ability, and everyday functioning. As the disease...
Heart failure at 25 cost her three limbs. Now she’s rebuilding her life with...
Working from her home in Phoenix, 25-year-old Alyssa Reader felt unusually anxious.
She put her marketing project aside and texted her mom, Natalie Reader, who...
Cannabis may distort memories more than people realize, study finds
Cannabis is often known for its relaxing effects, but scientists are increasingly studying how it affects the brain, especially memory. A new study from...
AI blood test could predict heart disease risk up to 15 years in advance
Heart disease remains the leading cause of death around the world. Every year millions of people die from conditions such as heart attacks, strokes,...
Too much or too little thyroid medicine could raise heart death risk
Thyroid problems are very common, and millions of people take medication every day to manage them. One of the most widely prescribed medicines for...
Some exercises can be risky for people with high blood pressure
Exercise is widely known as one of the best ways to keep the heart healthy. For many people, regular physical activity can help control...
Why many knee arthritis x-rays may do more harm than good
Osteoarthritis is one of the most common causes of long-term pain and disability. In Australia alone, more than two million people live with this...
Popular blood pressure drug may increase sudden cardiac arrest risk
High blood pressure is one of the most common health problems in the world. It affects hundreds of millions of people and greatly increases...
New cholesterol drug offers hope for people who cannot take statins
Cholesterol is a fatty substance that exists in every cell of the human body. It plays an important role in helping the body function...
Common blood pressure drug may harm kidneys and reduce potassium levels
High blood pressure is one of the most common health problems in the world. Doctors often call it hypertension. It happens when the force...
A simple vitamin could help immune system kill cancer
Cancer is one of the most serious health problems in the world. Every year, millions of people are diagnosed with different forms of cancer....
This overlooked blood pressure number may predict dementia risk
Many people know that high blood pressure can damage the heart, but fewer people realize that it can also harm the brain. Blood pressure...
Vitamin D2 supplements may have a hidden health risk
Vitamin D is one of the most popular dietary supplements in the world. Many people take it to keep their bones strong, support their...
Silent warning signs of heart valve disease you need to know
Heart valve disease is a condition that happens when one or more of the valves in the heart stop working properly. The human heart...
Week's Top
Editors Picks
New material could replace indium in displays and solar cells
Scientists have developed a new type of transparent electrode that avoids the use of indium, a rare and expensive metal widely used in modern...
Did the first land plants accidentally trigger two ancient ocean extinctions?
Hundreds of millions of years ago, the first plants began spreading across Earth’s land. This major turning point helped transform the planet into the...
Scientists unlock sulfur’s potential for cheaper, high-capacity EV batteries
As electric vehicles and electric aircraft become more common, the world’s demand for lithium-ion batteries is rising rapidly.
According to S&P Global Insights, battery demand...
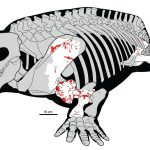
Fossil bite marks reveal ancient predator hunts 280 million years ago
New research suggests that large land predators were already hunting big plant-eating animals more than 280 million years ago, much earlier than scientists once...
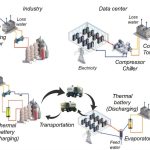
A simple mineral could help solve the data center energy crisis
Data centers are the backbone of the modern internet.
They store photos, stream movies, power cloud services, and train artificial intelligence systems.
But these warehouse-sized buildings...