Earth & Environment
Why many middle‑aged Americans feel worse than previous generations
A growing number of Americans in their 50s and early 60s say they feel lonelier, more depressed, and physically weaker than people of the...
Why dance tracks dominate TikTok while love songs rule Spotify
What makes a song become a hit today?
While listeners certainly play a role, new research suggests that streaming platforms and their algorithms also have...
US is less prone to oil price shocks than in past decades
Oil is a global market, so when prices rise in one place, they rise everywhere. The current war against Iran has already raised oil...
Scientists grow chickpeas in “moon dirt,” opening the door to farming on the Moon
As NASA prepares for future missions that could send astronauts back to the Moon, scientists are trying to answer an important question: what will...
Elephants steer clear of humans much more than other wildlife, study finds
Wild animals do not all react to human activity in the same way.
A new study from Botswana shows that some species are much more...
Antarctica has lost ice the size of 10 Los Angeles cities in 30 years
A new 30-year study has revealed how Antarctica’s ice is slowly retreating along parts of its vast coastline.
Scientists led by researchers at the University...
Did the first land plants accidentally trigger two ancient ocean extinctions?
Hundreds of millions of years ago, the first plants began spreading across Earth’s land. This major turning point helped transform the planet into the...
Fossil bite marks reveal ancient predator hunts 280 million years ago
New research suggests that large land predators were already hunting big plant-eating animals more than 280 million years ago, much earlier than scientists once...
Mars Express reveals a landscape filled with ancient craters on the red planet
A new image captured by the Mars Express orbiter offers a striking view of one of the most heavily cratered regions on Mars.
The image...
Wildfire smoke may trigger more severe strokes
Air pollution is often thought of as a long‑term environmental problem, but new research suggests that even short bursts of polluted air may have...
Study finds doctors more likely to die at home
Many people wonder whether doctors make different choices about medical care at the end of life.
Because physicians understand diseases, treatments, and hospital systems better...
‘Forever chemicals’ may speed up aging in middle-aged men
Chemicals known as PFAS, often called “forever chemicals,” are found in many everyday products, from non-stick cookware and waterproof clothing to food packaging and...
FEATURED
Yes, the odds of an asteroid striking Earth have doubled. No, you don’t need...
At the end of 2024, astronomers detected an asteroid in the night sky.
It was given the designation Y, since it was discovered in the...
Threads is latest social media option, but raises privacy concerns
Threads, a new Meta social media platform that launched this week, is giving users—already surpassing more than 30 million people—an alternative to Twitter.
Nazanin Andalibi,...
Scientists unravel the mystery of extreme waves
Ocean waves up to 30 meters that seemingly appear at random have long inspired legend and stumped scientists.
Now, researchers at the University of Sydney...
Air pollution may increase depression and suicide risk
In a new study, researchers found that people exposed to higher levels of air pollution are more likely to experience depression or die by...
People with certain genes were more likely to survive the Black Death, shows study
The Black Death was the single greatest mortality event in recorded history, killing up to 50% of the European population in less than five...
How toxic molds, fossil fuels, antibiotics could trigger chemical intolerance
You may not have heard of chemical intolerance (CI), but it's a condition that many Americans live with.
A recent study sheds light on how...
Scientists discover perfectly preserved dinosaur skin in Korea
In a new study, scientists found perfectly preserved dinosaur skin in South Korea.
They discovered a set of very small tracks with perfect skin traces...
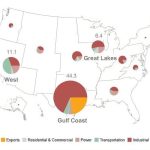
Texas’ growing hydrogen industry needs a lot of water, study finds
Hydrogen is a clean energy source that can be made in different ways, but all methods require large amounts of water.
A new study from...