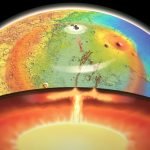
Largest earthquake on Mars revealed possible past meteoroid impact
The quake lasted four hours and identified layering in the crust that could indicate a meteoroid impact.
The 4.7 magnitude temblor happened in May 2022...
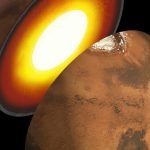
Mars is not a dead planet. It’s more active than previously thought
Mars, like Earth and Venus, possesses an active interior, which challenges current views on the evolution of the red planet.
Mars once had enough water for a planet-wide ocean 300 meters deep, shows study
Today, Mars is colloquially known as the “Red Planet” on a count of how its dry, dusty landscape is rich in iron oxide (aka....
Mars was covered by a 300-meter-deep ocean 4.5 billion years ago
When Mars was a young planet, it was bombarded by ice asteroids delivering water and organic molecules necessary for life to emerge.
This means...
Early crust on Mars is more complex than thought
Early crust on Mars may be more complex than previously thought—and it may even be similar to our own planet’s original crust.
The Martian surface...
Scientists use deep planetary scan to confirm Martian core?
Scientists from The Australian National University (ANU) have developed a new method to scan the deep interior of planets in our solar system to...
Two major meteorite impacts reveal new insights about Martian crust
Following two large meteorite impacts on Mars, near-surface seismic waves have been recorded for the first time on a planet other than Earth.
The...
Mars shows signs of life and youth
Until now, Mars has been generally considered a geologically dead planet.
An international team of researchers led by ETH Zurich now reports that seismic...
Ancient bacteria might lurk beneath Mars’ surface, shows study
New study finds the chances of uncovering life on Mars are better than previously expected
When Mars’ first samples return to Earth, scientists should be...
Rover findings offer glimpse of ancient landscape on Mars
CU Boulder geologist Lisa Mayhew is among the scientists working to recreate the history of an ancient landscape that wouldn’t look out of place...