A team of scientists from Nagoya University in Japan has created a powerful new cooling device that could change the future of smartphones and tablets.
This ultra-thin invention helps keep mobile devices cool—even during heavy use—without adding any bulk, allowing for slimmer designs and better performance.
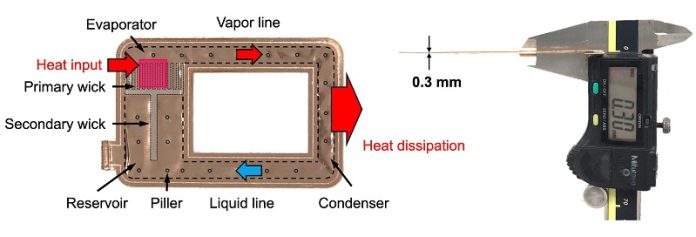
Their creation, called an ultra-thin loop heat pipe (UTLHP), is only 0.3 millimeters thick, yet it can handle high levels of heat.
It’s designed to solve a growing problem in modern electronics: the more powerful our devices get, the hotter they become.
Without proper cooling, this heat can slow devices down, shorten their lifespan, and even cause safety risks.
Traditional heat pipes are already used to manage heat in electronics, but they have limits when it comes to thin, compact devices.
The loop heat pipe works differently. It has a closed-loop system where a special liquid absorbs heat, turns into vapor, moves to a cooler part of the pipe, condenses back into liquid, and starts the cycle again.
It does all this without using electricity. Instead, it relies on a sponge-like material inside—called a wick—that moves the liquid around through capillary action.
In this new version, the researchers built the heat pipe using very thin copper sheets. They filled the inside with water and welded the parts together using lasers to keep the structure solid and leak-proof.
They also optimized the design from the beginning using computer models to make it compact and easy to add to existing smartphones.
Tests showed that this new pipe can move 10 watts of heat, which is more than enough to handle tasks like gaming, video editing, and other demanding apps. Even when the phone is held in different positions, the pipe works just as well.
In fact, it performs about 45 times better than regular copper in terms of heat transfer, and 10 times better than graphite, which is also known for its excellent cooling abilities.
An added bonus is that the device matches the size standards for smart cards, meaning it could also be used in contactless cards that need cooling, as they get more advanced.
According to Professor Hosei Nagano, this new cooling tech could help phones run longer and stay cooler, which may even extend battery life. Jun Sasaki, the lead researcher, explained that as our phones become more powerful, keeping them cool is more important than ever.
Thanks to this breakthrough, the future of mobile technology could be even faster, cooler, and thinner.
Source: KSR.



