Fires and accidents caused by counterfeit lithium-ion batteries are becoming a growing concern. These fake batteries are hard to distinguish from original ones based on their appearance alone.
Now, researchers at the University of Tsukuba have developed a simple, nondestructive method to verify a battery’s authenticity using magnetic sensors.
Lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) are essential in devices like smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles.
However, with their widespread use, battery shapes have become standardized, making it difficult to tell original equipment manufacturer (OEM) batteries apart from counterfeit ones.
While features like certification marks, QR codes, and IC chips are used for identification, these can often be copied.
To address this, researchers turned to the internal structure of batteries for a more reliable solution.
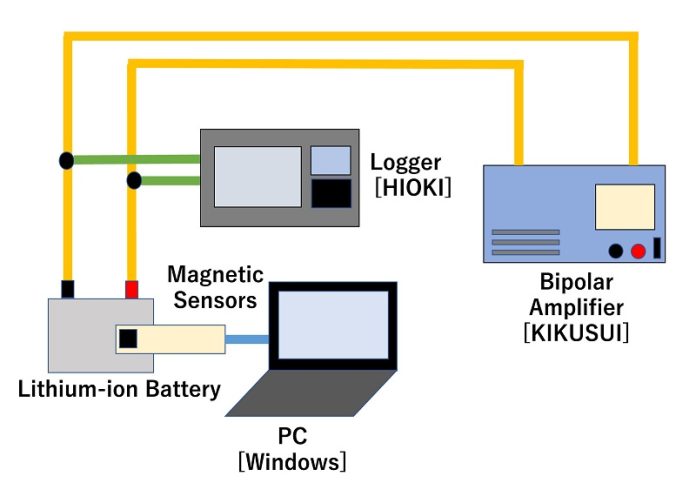
Their method involves attaching a magnetic sensor to the outside of a battery and measuring the magnetic field generated during charging or discharging.
Differences in the internal structure of batteries create unique magnetic fields, which the sensor can detect. This allows the system to identify both single cells and multiple connected batteries without damaging them.
This innovative approach builds on previous research by the team, who had earlier used magnetic sensors to detect issues in fuel cells.
In their latest study, published in Green Energy and Intelligent Transportation, the researchers successfully adapted the method to identify lithium-ion batteries.
The next steps for the team include developing a system that works within complete battery modules, as well as improving the technology to detect counterfeit batteries even when they have similar structures or show signs of wear and tear.
This nondestructive and reliable method could become an important tool for ensuring the safety and authenticity of lithium-ion batteries, protecting consumers and preventing accidents caused by counterfeit products.
Source: University of Tsukuba.



