A team of researchers from Shanghai Jiao Tong University and University College London has developed a groundbreaking energy system that could transform the future of shipping.
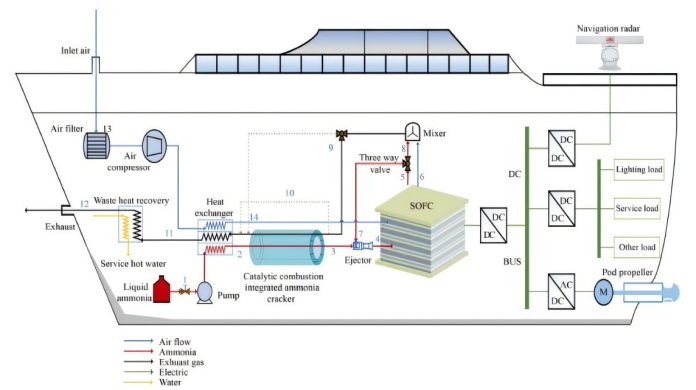
Using ammonia (NH3) as a fuel, this innovative solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) system offers an efficient and eco-friendly solution for powering all-electric ships.
Their study, published in Frontiers in Energy, addresses the urgent need to reduce carbon emissions in the maritime industry.
Shipping is responsible for a significant share of global carbon emissions. To tackle this, the International Maritime Organization has set a goal for 60% of new ships to use cleaner fuels like hydrogen (H2) or ammonia by 2060. Among these options, ammonia stands out as a promising alternative.
It’s inexpensive, nonflammable, and easy to store and transport. Unlike traditional fuels, it does not cause carbon buildup in engines, making it ideal for clean energy systems.
The researchers designed a new ammonia-powered SOFC system to overcome challenges such as slow hydrogen production and limited efficiency.
Central to their solution is a ribbed catalytic-combustion integrated ammonia cracker (IAC), which breaks down ammonia into hydrogen gas quickly and efficiently.
This innovative device can fully decompose ammonia in just 2.94 seconds, reducing the time and space needed for the process by 35% and 42%, respectively.
The experimental results are impressive. At 656°C, the system achieves 100% ammonia decomposition and powers the SOFC to produce 2.045 kW with an efficiency of nearly 59%. The noise level is just 58.6 decibels—similar to a conversation in a quiet room—and emissions of harmful gases like CO2, NO, and SO2 are almost zero.
The system is adaptable to different sailing conditions and meets the energy needs of a target ship with a rated power of 96 kW and an electrical efficiency of over 60%.
This breakthrough marks a significant step toward sustainable shipping. By using ammonia as a clean fuel, the system aligns with global efforts to combat climate change while addressing the technical challenges of green energy in maritime applications. The researchers believe this technology could lead to substantial reductions in ocean carbon emissions.
The new ammonia-fueled SOFC system not only demonstrates the potential of hydrogen-based shipping but also paves the way for a future where ships can operate with minimal environmental impact. This innovation could soon power the maritime industry into a cleaner, greener era.
Source: Frontiers Journals.



