Researchers from La Trobe University in Australia and Phillipps-University of Marburg in Germany have made a groundbreaking discovery on how to control blood vessel growth using a peptide called Apelin.
This finding, published in the journal Science Advances, opens up new possibilities for cancer treatment, organ regeneration, and tissue engineering.
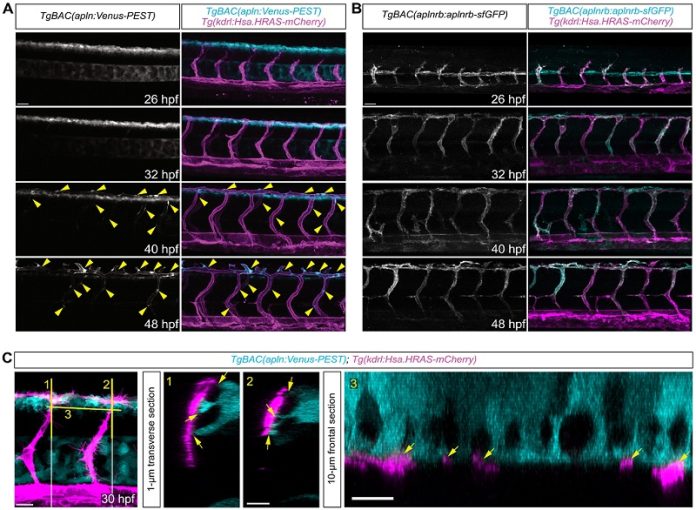
The study revealed that Apelin, produced by special stem cells in the nervous system called “neuro progenitor cells,” plays a key role in regulating the signals that control blood vessel growth. Dr. Kazuhide Shaun Okuda, a researcher at La Trobe University whose expertise in zebrafish research and imaging was crucial to this study, highlighted the potential impact of this discovery.
“Understanding how blood vessels develop could lead to new treatments to stop excessive blood vessel growth in diseases like cancer.
It could also lead to treatments in situations where promoting blood vessel growth is needed, such as organ regeneration and tissue engineering,” Dr. Okuda explained.
This is the first time that Apelin, one of several “growth factor” peptides secreted by various cells, has been shown to directly influence blood vessel development.
The research team discovered that Apelin not only stimulates but also regulates the growth of new blood vessels.
To make this discovery, the researchers studied blood vessel development in living zebrafish, which are transparent as embryos and young fish. This transparency allowed the team to observe the effects of Apelin on blood vessel growth in real time.
The ability to control blood vessel growth has significant implications for cancer treatment. Tumors often stimulate the growth of new blood vessels to supply them with nutrients, enabling their growth and spread.
By targeting Apelin, scientists may be able to develop new therapies to control or reduce this blood vessel growth, potentially limiting tumor progression.
Moreover, this discovery is vital for advancing research in organ regeneration and tissue engineering.
Both fields require the formation of blood vessels to support the growth and nourishment of new tissues. Understanding and manipulating Apelin’s role could improve techniques for regenerating damaged organs and engineering new tissues.
Dr. Okuda also noted the potential benefits of Apelin in cardiac regeneration. “There’s research that suggests it can help with cardiac regeneration, for example,” he said.
In summary, the discovery of Apelin’s role in blood vessel growth is a major scientific advancement.
It opens up new pathways for developing treatments for diseases characterized by abnormal blood vessel growth, like cancer, and for enhancing techniques in organ regeneration and tissue engineering.
If you care about heart health, please read studies about the best time to take vitamins to prevent heart disease, and calcium supplements could harm your heart health.
For more information about health, please see recent studies that blackcurrants can reduce blood sugar after meal and results showing how drinking milk affects risks of heart disease and cancer.



