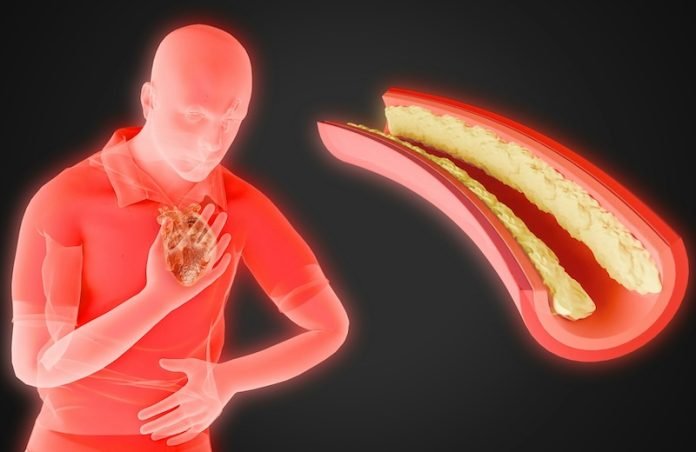
Atherosclerosis is a condition where the arteries, which carry blood from the heart to the rest of the body, become narrowed and hardened due to a buildup of plaque.
This plaque is made up of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances found in the blood. When plaque builds up in the arteries, it can restrict blood flow, leading to serious health problems such as heart attacks and strokes.
One of the main causes of atherosclerosis is high cholesterol. Cholesterol is a fatty substance that is necessary for building cells and producing certain hormones, but too much cholesterol in the blood can lead to plaque formation.
There are two types of cholesterol: low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL). LDL is often referred to as “bad” cholesterol because it contributes to plaque buildup, while HDL is known as “good” cholesterol because it helps remove cholesterol from the bloodstream.
Research has shown that high levels of LDL cholesterol and low levels of HDL cholesterol are associated with an increased risk of atherosclerosis.
High blood pressure, or hypertension, is another significant factor in the development of atherosclerosis. When blood pressure is consistently high, it can damage the inner lining of the arteries, making it easier for plaque to accumulate.
This damage can also cause the arteries to become less flexible, which further contributes to the hardening process. Studies have consistently demonstrated a strong link between hypertension and the risk of developing atherosclerosis and related cardiovascular diseases.
Smoking is a well-known risk factor for atherosclerosis. The chemicals in tobacco smoke damage the lining of the arteries, promote the buildup of plaque, and reduce the level of oxygen in the blood.
Smoking also raises blood pressure and lowers HDL cholesterol levels, creating a perfect storm for the development of atherosclerosis.
Research indicates that smokers are significantly more likely to develop atherosclerosis compared to non-smokers, and quitting smoking can greatly reduce this risk.
Diabetes, particularly type 2 diabetes, is closely linked to atherosclerosis. High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels and contribute to the formation of plaque.
People with diabetes often have other risk factors for atherosclerosis, such as high blood pressure and high cholesterol levels. Research has shown that individuals with diabetes are at a much higher risk of developing atherosclerosis and related complications.
A sedentary lifestyle and poor diet are also major contributors to atherosclerosis. Lack of physical activity can lead to obesity, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol levels, all of which increase the risk of atherosclerosis.
A diet high in saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol can contribute to plaque buildup in the arteries. Conversely, a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help reduce this risk.
Studies have found that regular exercise and a balanced diet can significantly lower the likelihood of developing atherosclerosis.
Genetics also play a role in atherosclerosis. People with a family history of heart disease are more likely to develop the condition themselves.
While you cannot change your genetic makeup, being aware of your family history can help you take preventive measures, such as maintaining a healthy lifestyle and monitoring your blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
In conclusion, atherosclerosis is a complex condition with multiple causes, including high cholesterol, high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, a sedentary lifestyle, poor diet, and genetics.
The good news is that many of these risk factors can be managed or even prevented through lifestyle changes. Eating a healthy diet, staying physically active, quitting smoking, and regularly monitoring your health can greatly reduce your risk of developing atherosclerosis and its serious complications.
By understanding the causes and taking proactive steps, you can protect your heart and maintain better overall health.
If you care about heart disease, please read studies that herbal supplements could harm your heart rhythm, and how eating eggs can help reduce heart disease risk.
For more information about heart health, please see recent studies that apple juice could benefit your heart health, and results showing yogurt may help lower the death risks in heart disease.
Copyright © 2024 Knowridge Science Report. All rights reserved.



