Regular exercise is important for heart health, but for individuals with heart disease, it’s crucial to exercise safely to prevent complications and promote cardiovascular well-being.
Let’s explore some important precautions and considerations for exercising with heart disease, supported by research evidence and plain language explanations.
Firstly, it’s important to understand the benefits of exercise for heart disease patients.
Regular physical activity can improve cardiovascular fitness, lower blood pressure, reduce cholesterol levels, manage weight, and enhance overall well-being.
Exercise can also help reduce the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular events in individuals with heart disease.
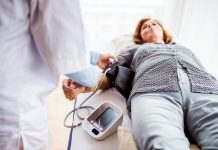
However, before starting an exercise program, it’s essential for individuals with heart disease to consult with their healthcare provider to determine their exercise capacity and any limitations or precautions they should take.
A comprehensive medical evaluation may include tests such as an exercise stress test, echocardiogram, or cardiac catheterization to assess heart function and identify any underlying conditions or risk factors that may affect exercise safety.
Once cleared by their healthcare provider, individuals with heart disease can begin an exercise program tailored to their needs and abilities. It’s important to start slowly and gradually increase the intensity, duration, and frequency of exercise over time.
A combination of aerobic exercise (such as walking, cycling, swimming, or dancing) and strength training exercises (such as lifting weights or using resistance bands) is recommended for overall cardiovascular fitness and muscle strength.
Research evidence suggests that regular exercise is safe and beneficial for individuals with stable heart disease, including those who have had a heart attack, coronary artery bypass surgery, or angioplasty with stent placement.
A meta-analysis published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology found that structured exercise training was associated with reductions in mortality and cardiovascular events in individuals with coronary artery disease.
However, certain precautions should be taken when exercising with heart disease to minimize the risk of complications.
Individuals with heart disease should avoid high-intensity or strenuous activities that may strain the heart, such as heavy lifting, sprinting, or competitive sports.
Instead, focus on moderate-intensity activities that elevate the heart rate and breathing rate without causing excessive fatigue or discomfort.
Furthermore, individuals with heart disease should pay attention to warning signs or symptoms during exercise, such as chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, dizziness, lightheadedness, palpitations, or nausea.
If any of these symptoms occur, it’s important to stop exercising immediately and seek medical attention if necessary.
Research has shown that early recognition and prompt treatment of cardiovascular symptoms during exercise can help prevent serious complications and improve outcomes for individuals with heart disease.
In addition to exercise precautions, individuals with heart disease should also consider other factors that may affect exercise safety, such as environmental conditions (such as extreme heat or cold), medication side effects, and hydration status.
Staying hydrated, wearing appropriate clothing and footwear, and exercising in a safe and comfortable environment can help minimize the risk of exercise-related complications.
In summary, exercising safely with heart disease requires careful consideration of individual needs, abilities, and precautions.
By working closely with their healthcare provider and following personalized exercise recommendations, individuals with heart disease can enjoy the benefits of regular physical activity while minimizing the risk of complications.
Remember to start slowly, listen to your body, and seek medical attention if you experience any warning signs or symptoms during exercise. With the right precautions and guidance, exercise can be a safe and effective way to improve heart health and overall well-being for individuals with heart disease.
If you care about heart health, please read studies about how drinking milk affects risks of heart disease, and herbal supplements could harm your heart rhythm.
For more information about heart health, please see recent studies about how espresso coffee affects your cholesterol level, and results showing Vitamin K2 could help reduce heart disease risk.
Copyright © 2024 Knowridge Science Report. All rights reserved.