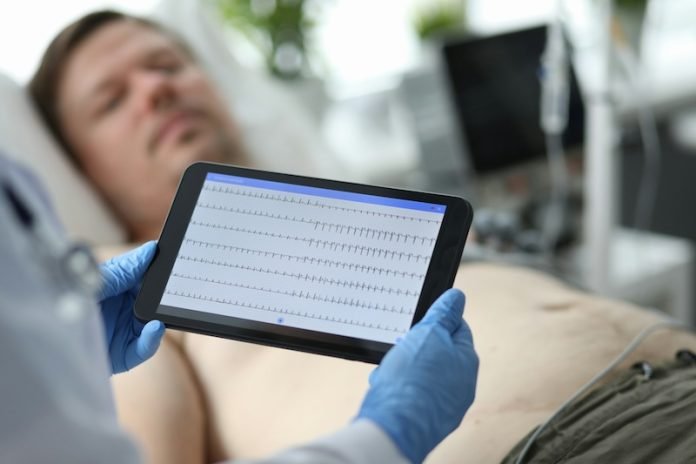
At the Mayo Clinic, a pioneering approach is redefining how we detect and monitor heart disease.
Utilizing artificial intelligence (AI) technology, researchers and clinicians are enhancing the capabilities of a tool that’s been a staple in diagnosing heart conditions for over a century—the electrocardiogram (ECG).
This innovative use of AI could lead to earlier detection of heart disease, potentially saving lives and improving patient outcomes.
Heart disease often reveals itself through significant, sometimes catastrophic events like heart attacks, strokes, or cardiac arrest. Early detection is crucial for improving a patient’s quality of life and longevity, yet the absence of clear symptoms complicates this goal.
The AI-enabled ECG emerges as a solution, offering a way to detect heart disease earlier and monitor its progression. This method is not only relatively inexpensive and widely available but often already integrated into a patient’s electronic health record.
Mayo Clinic’s development of ECG-AI algorithms marks a significant advance in cardiac care.
These algorithms are currently being used in research settings to predict the likelihood of various heart conditions, such as atrial fibrillation, amyloidosis, aortic stenosis, low ejection fraction, and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM).
Remarkably, the AI can also determine a patient’s biological age using ECGs from both traditional 12-lead setups and single-lead devices like smartwatches.
One notable application of this technology is its use in detecting low ejection fraction, a condition indicative of a weak heart pump.
This algorithm has received clearance from the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for clinical use and is being developed commercially.
It signifies a leap forward in diagnosing conditions that, if untreated, could lead to severe heart failure or necessitate a heart transplant.
The implications of AI in cardiac care extend beyond mere diagnosis. For instance, in the case of peripartum cardiomyopathy—a heart condition that can develop during or shortly after pregnancy—the AI-enabled digital stethoscope, capable of capturing single-lead ECG and heart sounds, has shown potential to significantly increase detection rates.
This technology could be particularly life-saving for women in underserved populations, where access to advanced diagnostics is limited.
Moreover, AI’s role in identifying amyloidosis, a rare but treatable condition characterized by protein deposits in the heart, underscores its potential to revolutionize early diagnosis and treatment.
The ease and affordability of ECG-AI mean it could be a game-changer for detecting amyloidosis and other conditions worldwide, especially in areas where healthcare resources are scarce.
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), a common genetic heart disease, is another area where AI is making strides. Early detection of HCM is challenging, as it often goes unnoticed until it becomes severe.
AI’s ability to identify subtle patterns on an ECG that might be missed by human eyes offers hope for early diagnosis, not just for the patient but potentially for at-risk family members as well.
Mayo Clinic’s pioneering use of AI in enhancing ECG diagnostics is a testament to the potential of technology to transform healthcare.
By making early detection more accessible and accurate, AI is opening new avenues for treating and managing heart disease, with the promise of better outcomes and longer lives for patients around the globe.
If you care about heart health, please read studies about how eating eggs can help reduce heart disease risk, and herbal supplements could harm your heart rhythm.
For more information about health, please see recent studies that olive oil may help you live longer, and vitamin D could help lower the risk of autoimmune diseases.
Copyright © 2024 Knowridge Science Report. All rights reserved.