Scientists have developed a groundbreaking technique that could revolutionize the discovery and development of treatments for autoimmune diseases such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
These conditions and transplant cell failures are caused by changes in cytokine secretion by immune cells in the human body.
Researchers must identify the genetic regulators of cytokine secretion to find effective treatments for these diseases.
An international team of researchers has introduced a novel method called Secretion-Enabled Cell Ranking and Enrichment (SECRE).
They have demonstrated its accuracy in sorting CRISPR-edited cells based on their secretion patterns and identifying the genetic regulators of cytokine secretion in autoimmune conditions.
Additionally, the technique considers detailed profiles of approved and experimental treatments to explore new therapeutic applications.
This research, conducted over approximately four years by scientists from the UK, US, and Canada, offers hope for millions of people affected by these conditions. The study validated SECRE’s potential to identify treatment options for autoimmune diseases.
In particular, it examined its impact on inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), a condition with no known cure that affects an estimated seven million people globally.
As part of their validation, researchers investigated the effect of various kinase inhibitors, including XMU-MP1, on CD4+ T cells, which produce interferon gamma, a protein implicated in autoimmune diseases.
XMU-MP1, previously explored for heart failure and other conditions, demonstrated significant promise in reducing colitis symptoms in mice with a similar cell secretion profile to humans with IBD.
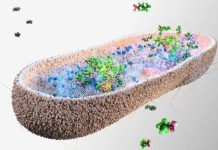
The SECRE technique captures secreted cytokines on cell surfaces, labels them with magnetic nanoparticles, and sorts them within a microfluidic device using 3D printing technology.
This approach allows for high-resolution sorting of cells based on secretion patterns, making it suitable for large-scale genetic screens. It also enables the selective sorting of immune cell subsets based on specific markers and secretion factors.
While further clinical trials are needed before this technique can be considered for widespread use, its potential to discover new treatments for autoimmune diseases offers hope for improved patient outcomes and quality of life.
If you care about health, please read studies about how Mediterranean diet could protect your brain health, and the best time to take vitamins to prevent heart disease.
For more health information, please see recent studies that olive oil may help you live longer, and vitamin D could help lower the risk of autoimmune diseases.
The research findings can be found in Nature Biomedical Engineering.
Copyright © 2023 Knowridge Science Report. All rights reserved.