Ever heard of hydrogen fuel cells?
They’re a game-changer because they offer a clean way to generate electricity. Unlike batteries that run out and need to be charged, fuel cells keep going as long as they have fuel—in this case, hydrogen gas.
While already eco-friendly, there’s room for improvement, and that’s exactly what a team of scientists at UNIST has done.
Led by Professor Myoung Soo Lah, the researchers found a way to make these hydrogen fuel cells more efficient by focusing on a crucial part known as the “solid electrolyte.”
This component helps hydrogen ions move around, which is essential for creating electricity.
Typically, hydrogen fuel cells use a material called Nafion in the solid electrolyte. While Nafion is good at conducting hydrogen ions, it has some limitations, such as not being ideal in extreme temperatures.
Researchers at UNIST decided to experiment with a different material called Metal-Organic Frameworks, or MOFs for short. Imagine MOFs as tiny sponges made up of metal and organic material.
These minuscule sponges have a porous structure, meaning they have tiny holes that can be filled with other substances to make them even more effective.
MOFs are known for their versatility and stability. They can be used in various applications and are stable in both high and low temperatures, making them excellent candidates for fuel cells.
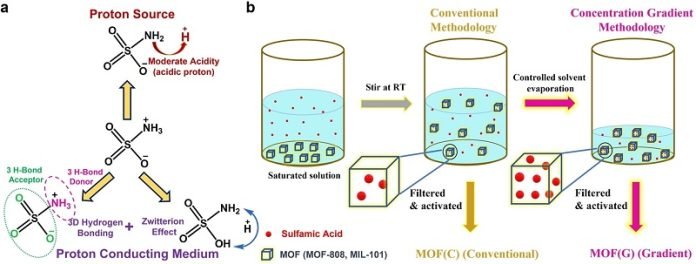
In this groundbreaking study, the researchers introduced a unique kind of molecule known as “zwitterionic sulfamic acid” into these MOFs.
This special molecule has both positive and negative charges and is excellent at forming bonds with hydrogen.
By packing more of this molecule into the holes in the MOFs, the team developed a solid electrolyte that enables the quick movement of hydrogen ions.
This faster ion movement means that the fuel cells can produce electricity more efficiently. Additionally, the new material remained effective for an extended period, adding a layer of reliability that is crucial for real-world applications.
This research holds great promise for enhancing the efficiency of hydrogen fuel cells, which are a critical part of the move towards more sustainable energy solutions.
As the world grapples with climate change, cleaner methods of producing energy are more important than ever. Better hydrogen fuel cells could mean more electricity generated in a cleaner way, helping us take better care of the planet.
The study is a significant step toward achieving more efficient, reliable, and eco-friendly energy solutions, aligning with global efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and slow down climate change.
So the next time you hear about hydrogen fuel cells, know that not only are they a good option for the environment, but they’re also getting better and more efficient, all thanks to some brilliant science.
The study was published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition.
Follow us on Twitter for more articles about this topic.
Source: Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology.