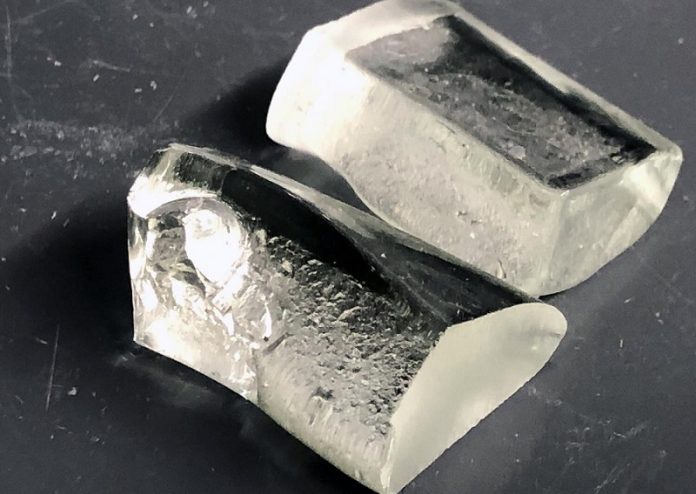
Researchers at Penn State University have developed an innovative glass called LionGlass, which holds the promise of revolutionizing glass manufacturing.
This breakthrough material not only cuts the carbon footprint of glass production by nearly half but also boasts remarkable strength and crack resistance.
Let’s delve into the world of LionGlass and discover how it could shape a more sustainable future.
Glass is an ancient material that has played a crucial role in shaping modern civilization for over 5,000 years.
Now, scientists have developed a groundbreaking type of glass called LionGlass, which aims to make glass manufacturing more sustainable while offering unprecedented strength.
Traditional glass, known as soda lime silicate glass, is commonly used in everyday items like windows and glassware.
However, its production process releases vast amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2), a greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change. LionGlass, on the other hand, eliminates the need for carbon-containing materials, resulting in a significant reduction in CO2 emissions.
The secret lies in LionGlass’s lower melting temperature, which requires less energy compared to conventional glass production. By lowering the melting temperature by 300 to 400 degrees Celsius, LionGlass reduces energy consumption by approximately 30%.
This reduction in energy usage translates to a substantial decrease in greenhouse gas emissions, making LionGlass an environmentally friendly alternative.
But LionGlass isn’t just eco-friendly; it’s also remarkably robust. In fact, the researchers were amazed to discover that LionGlass exhibited significantly higher crack resistance than standard glass.
Some compositions of LionGlass were found to withstand even a one-kilogram force from a diamond indenter, while conventional glass typically cracks under a 0.1-kilogram force. This exceptional crack resistance makes LionGlass invaluable in various industries, from automotive and electronics to architecture and healthcare.
The durability of LionGlass is crucial because cracks are the primary cause of glass failure. Over time, microcracks develop on the surface of glass, weakening the material.
When glass breaks, it’s often due to the presence of these microcracks. LionGlass’s exceptional resistance to microcrack formation means it can withstand more stress, making it safer and longer-lasting.
Furthermore, the enhanced strength of LionGlass opens up possibilities for lighter and more efficient products. Given that LionGlass is ten times more crack-resistant than traditional glass, it can be significantly thinner while maintaining the same level of durability.
This reduction in weight not only minimizes the raw materials required but also decreases energy consumption during transportation, benefitting both the environment and various industries.
The research team is continuously exploring the potential of LionGlass and has filed a patent application for the glass family. Within this family, various compositions of LionGlass possess distinct properties and applications.
The researchers are subjecting different LionGlass compositions to diverse chemical environments to study their reactions, aiming to develop a comprehensive understanding of LionGlass’s versatility and widespread use.
Glass has a vital role to play in addressing global challenges such as environmental issues, renewable energy, energy efficiency, healthcare, and urban development. With LionGlass, the future of glass manufacturing appears brighter, paving the way for a sustainable and resilient world.
LionGlass, an innovative glass developed by researchers at Penn State University, has the potential to revolutionize the glass industry. By significantly reducing carbon emissions and offering unparalleled strength and crack resistance, LionGlass presents a sustainable solution for the future.
This breakthrough material not only contributes to environmental conservation but also holds immense promise for a wide range of industries, from automotive and electronics to healthcare and beyond. The development of LionGlass marks an exciting step towards a greener and more resilient world.
Follow us on Twitter for more articles about this topic.