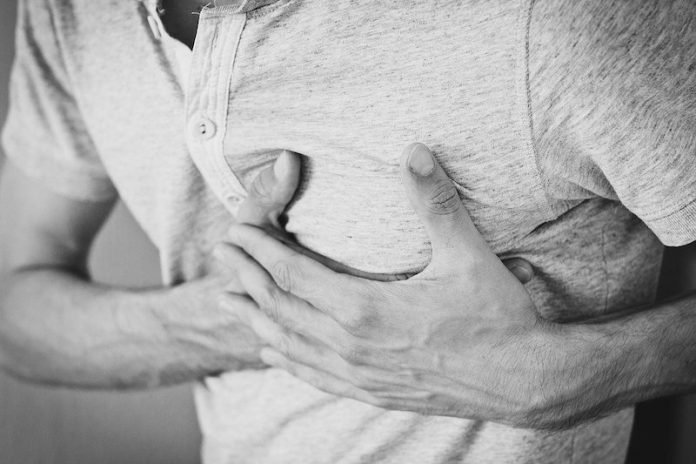
In a new study, researchers have made a key discovery as to why we become more susceptible to heart disease as we age.
The human body, especially the heart, is dependent on the mitochondria, the part of the cell responsible for producing energy to maintain organ function.
The protein, Sesn2, is located inside the mitochondria and plays a pivotal role in protecting the heart from stress.
The researchers found levels of Sesn2 diminish over time, which weakens the heart and can cause it to lose functionality.
They found that an insufficient level of Sesn2 is the reason older individuals are at greater risk of heart attack and other heart complications.
This shows stabilizing the protein could be the answer to maintaining a healthy heart.
The research was conducted by a team at the University of South Florida and elsewhere.
It’s common for people who’ve experienced cardiac arrest to have a stent inserted into a blood vessel to relieve an obstruction or are prescribed medications designed to prevent blood clots.
While they may offer rapid relief, these treatments can cause further injury to the heart. There are currently no known treatments available to prevent those potential side effects.
In the study, the team found focusing on Sesn2 can keep mitochondria functional integrity, offsetting such complications.
Through biochemical analysis and high-powered microscopes, they could see Sesn2 deficiency caused cells to die, inducing a heart attack.
The team says the age-related Sesn2 is a critical player in mitochondria. Maintaining cardiac Sesn2 levels could make the heart energetic and against age-related heart disease.
One author of the study is Dr. Ji Li, professor of surgery and molecular pharmacology and physiology.
The study is published in Redox Biology.
Copyright © 2020 Knowridge Science Report. All rights reserved.