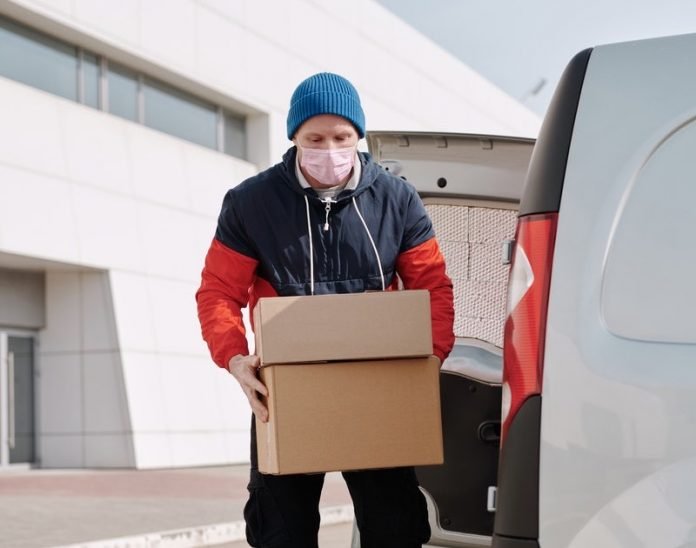
In a new study, researchers found that as many as 74 million essential workers and their families are at increased risk for COVID-19 in the U.S.
Of that number, up to 61% are at increased risk for severe COVID-19.
The research was conducted by a team from the U.S. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
Public policymakers face important decisions about how to balance the economic benefits of keeping workers employed and the public health benefits of protecting those with increased risk of severe COVID-19.
These issues are important when deciding to close segments of the economy and how to distribute vaccines, which will initially be available only in limited supply.
In the study, the team also looked at the increased risk for COVID-19 among those living with essential workers who could not work at home.
Many parts of the United States face rising infection rates.
The researchers used data collected before the pandemic to examine how many workers were in essential jobs, how often they were able to work at home, their risk of severe COVID-19 outcomes in the event they are infected, and the health risks of their household members
They found that 72% of all workers were in jobs deemed essential, and over three-quarters of all essential workers were unable to work at home.
Not only that, but as many as 61% of these workers had underlying health issues that put them at increased risk of severe COVID-19 should they become infected.
The risks to essential workers in all disciplines who could not work from home were clear from the beginning of the pandemic, the team says.
But the risk of transmission to household members living with essential workers became equally important when considering the potential for disease progression along with community transmission.
Since scientists know that asymptomatic transmission of the virus is a major way it spreads, steps like self-isolation and self-quarantining in separate rooms in the home, along with wearing masks, might reduce the risk of transmission.
One author of the study is Thomas Selden.
The study is published in JAMA Internal Medicine.
Copyright © 2020 Knowridge Science Report. All rights reserved.