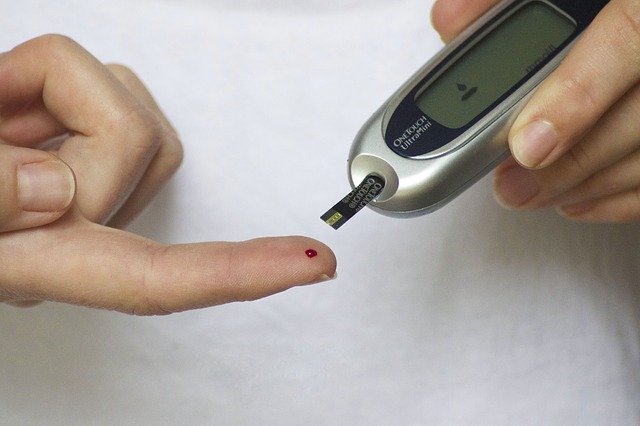
In a new study, researchers found that saliva could be used instead of blood to control diabetes.
The test was developed as an alternative to the current prevalent practice of monitoring blood glucose. Lab tests of the saliva process had an accuracy rate of 95.2%.
The research shows promising results for monitoring diabetes, which affects an estimated 425 million people worldwide—around half of them undiagnosed.
The research was conducted by a team at the University of Strathclyde and elsewhere.
Frequent monitoring of diabetes is essential for improved glucose control and to delay clinical complications related to the condition.
Early screening is also paramount in reducing these complications worldwide.
Blood analysis for screening, monitoring, and diagnosing diabetes is widely practiced but is quite invasive and painful.
The constant need to piercing the fingers several times daily for most patients may lead to the development of finger calluses, as well as difficulty in obtaining blood samples; furthermore, not everyone would want to give blood and there are circumstances in which it could be dangerous.
In the study, the lab tests used a scientific system known as Attenuated total reflectance Fourier transform infrared (ATR-FTIR) spectroscopy.
This has been used in the diagnosis of several diseases, although its applications in the monitoring of diabetic treatment have begun to emerge only recently.
Samples were assessed in three categories—diabetic, non-diabetic and insulin-treated diabetic—and two potential diagnostic biomarkers were identified.
The team says saliva reflects several physiological functions of the body, such as emotional, hormonal, nutritional and metabolic, and so its biomarkers could be an alternative to blood for robust early detection and monitoring.
It is easy to collect, non-invasive, convenient to store and requires less handling than blood during clinical procedures, while also being environmentally efficient.
It also contains analytes with real-time monitoring value which can be used to check a person’s condition.
The researchers are hopeful that the process they have developed could be used for both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes, although further study will be required to confirm this.
The lead author of the study is Dr. Matthew Baker, a Reader in Strathclyde’s Department of Pure and Applied Chemistry.
The study is published in PLOS ONE.
Copyright © 2020 Knowridge Science Report. All rights reserved.



