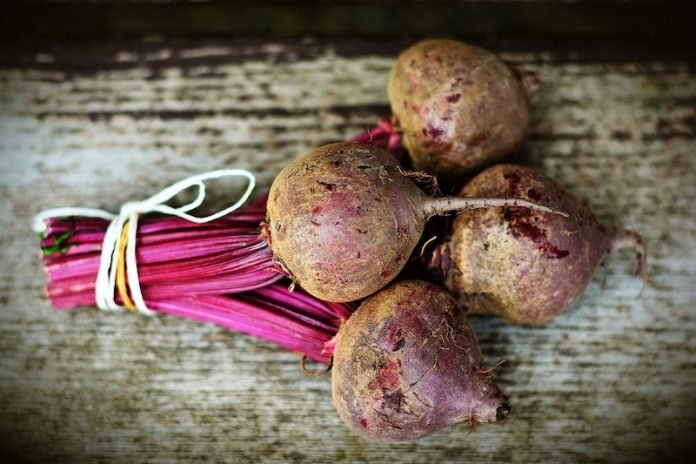
In a new study, researchers found that eating a small amount of beetroot in a salty diet may help prevent high blood pressure.
They also found that dietary nitrate supplements have similar health benefits.
The research was conducted by a team from UCSF.
Many people eat about twice the recommended level of salt in their daily diet.
This makes the level of sodium in their body very high. These people are more likely to have high blood pressure and increased risk of heart disease and stroke.
One way to solve the problem is to eat more potassium-rich fruits and vegetables, which can lessen the effects of sodium on cardiovascular health.
However, many people don’t follow the suggestion. It is important to find new ways to prevent salt-induced high blood pressure.
In the current study, the team fed salt-sensitive rats salt along with small amounts of beetroot juice or dietary nitrate.
Dietary nitrate can be found in the root and leafy vegetables such as spinach, lettuce, and celery.
The results showed that both the juice and the nitrate supplement were more than 100 times more potent than potassium in protecting against salt-induced high blood pressure.
The team suggests that this may provide a new method for reducing salt-induced high blood pressure simply by adding a nitrate concentrate to certain salty foods.
Future work will test the method on humans to see if simply eating beetroot or dietary nitrate could help fight high blood pressure.
They also suggest that people who need to control blood pressure should eat diets rich in fruits and vegetables, such as the Mediterranean diet or the DASH diet.
Both diets could help prevent heart disease and stroke. Root and green, leafy vegetables are features of the DASH diet.
The lead author of the study is Dr. Theodore W. Kurtz, a professor of laboratory medicine at UCSF.
The study is published in the journal Hypertension.
Copyright © 2019 Knowridge Science Report. All rights reserved.