In a new study, researchers found a possible connection between the intensity of oil and gas exploration in an area and early indicators of cardiovascular disease among nearby residents.
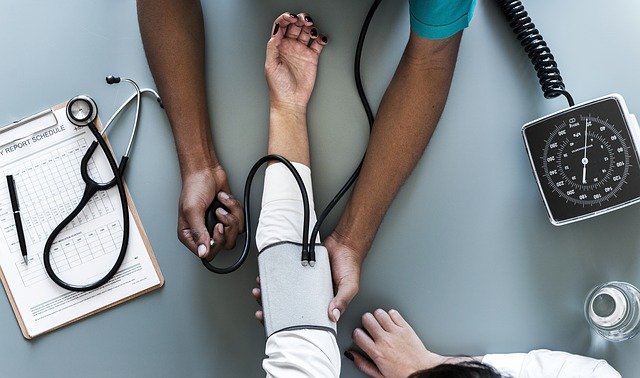
From Oct. 2015 to May 2016, the researchers measured indicators of CVD in 97 men and women from Fort Collins, Greeley and Windsor who did not smoke tobacco or marijuana.
The scientists found that those who lived in areas of more intense oil and gas development showed early signs of cardiovascular disease (CVD).
This study is the first to investigate the relationship between oil and gas development and CVD.
It was conducted by a research team at the Colorado School of Public Health.
CVD is the leading cause of mortality in the U.S. with more than 900,000 deaths in 2016.
CVD includes higher blood pressure, changes in the stiffness of blood vessels, and markers of inflammation.
The researchers are not sure whether the responsible factor is noise or emissions from the well pads or something else, but they did observe that with more intense oil and gas activity around a person’s home, cardiovascular disease indicator levels increased.
More than 17.4 million people in the U.S. now live within one mile of an active oil and gas well.
Previous studies have shown that short and long-term exposure to the kind of particulate matter emitted from oil and gas operations may be associated with increases in cardiovascular disease and death.
In the study, the participants did not have jobs that exposed them to dust, fumes, solvents or oil or gas development activities.
None had histories of diabetes, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or chronic inflammatory diseases like asthma or arthritis.
The team suggests that while behavioral and genetic factors contribute to the burden of CVD, exposure to environmental stressors, such as air pollution, noise and psychosocial stress also contribute to cardiovascular morbidity and mortality.
One increasingly common source of these stressors is an extraction of oil and gas in residential areas.
Advances in fracking, horizontal drilling, and micro-seismic imaging have opened up many previously inaccessible areas for exploration. Some of those wells are in heavily populated areas.
At the same time, noise levels measured in communities near these facilities have exceeded levels associated with increased risk of CVD and hypertension.
But the results are consistent with an increase in the frequency of cardiology inpatient hospital admissions in areas of oil and gas activity in Pennsylvania.
The study findings support the use of these indicators of cardiovascular disease in future studies on oil and gas development in residential areas.
Those indicators included blood pressure, arterial stiffening and early markers of inflammation.
McKenzie acknowledged the limitations of the small sample size, saying that the results demonstrate the need for a much larger study.
The study’s lead author Lisa McKenzie, Ph.D., MPH, of the Colorado School of Public Health at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus.
The study is published in the journal Environmental Research.
Copyright © 2018 Knowridge Science Report. All rights reserved.
Source: Environmental Research.



